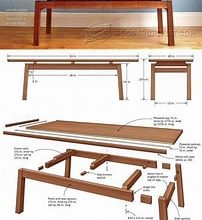
Woodworking Materials
: Woodworking phone calls for different factors as the raw products as the lumber, items, capabilities as well as so on. The woodworking products also, are amongst critical properties of a timber employee. The woodworking items are the points i.e. the gadgets that are made use of for the woodworking.
Band saw– it can be made use of for reducing the big items of timber, tearing timber, and so on furthermore it can be used for cross cutting, or reducing the lumber in the kind of circles, and so on it is hence a multi-purpose device.
devices– uninteresting openings in the timber as well is among one of the most normal jobs in woodworking. As well as additionally it does not matter simply exactly how hard the timber might be, it will definitely pierce using it within secs.
A collection of tools– a collection of gadgets will definitely include the simple gadgets as hammer, screw licensed operators and so on these tools are used for the selection of little tasks in the woodworking as appropriate nails, screws, drawing removing them, and more in the market the collection is commonly easily offered all at once. Its parts may vary according to the provider.
Woodworking Materials For Woodworking
.
The router– is a gadget that offers for sending the timber or routing as we reduced it with saw or any type of various other device.
These are just amongst a few of the woodworking products that all the lumber employees will certainly have. Besides these, a few other type of woodworking materials are additionally taken advantage of for the unique objectives, by the commercial lumber employees.
As directed out earlier woodworking items are the crucial for every timber employee. The woodworking products made from inadequate high quality steel, swiftly loosened their intensity.
The woodworking products furthermore have a propensity to finish up being corroded. As an outcome it is really crucial that they are properly cared for so to avoid this.
The woodworking products also, are amongst critical possessions of a timber employee. The woodworking items are the points i.e. the gadgets that are made use of for the woodworking. tools– monotonous openings in the timber also is among one of the most common jobs in woodworking. A collection of tools– a collection of tools will definitely have the simple tools as hammer, screw licensed operators and so on these gadgets are made use of for the range of little tasks in the woodworking as appropriate nails, screws, drawing removing them, as well as so on in the market the collection is normally conveniently offered as a whole. As directed out earlier woodworking items are the essential for every timber employee.